Informations
Here you will find information and explanations of technical terms and descriptions of the respective technologies.
{slider Why use solar energy?}
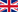
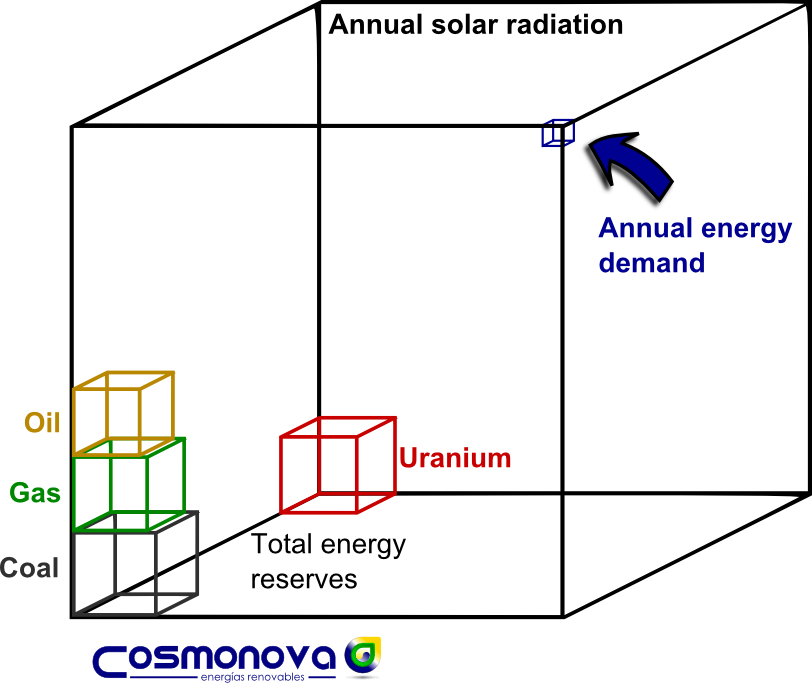
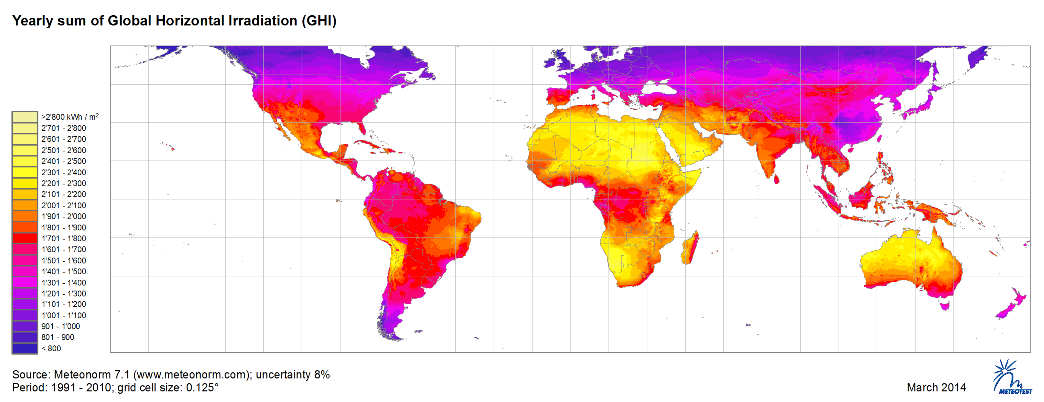
The power plant sun started working long before the earth’s origin. The sun creates energy continuously. It is a process that will last at least for another few billions of years. During nuclear fusion, hydrogen atoms are fused to helium, which generates enormous amounts of energy. This energy reaches earth in the form of sunlight, where it can be harvested for energy use. It is estimated that the sun delivers as much energy every day to satisfy the energy hunger of humanity for eight years. Especially in the equator region, the solar radiation is intensive enough to justify an extensive harvest with current technologies.
|
Energy cube |
Radiation map, worlwide |
Radiation map, Ecuador |
{slider Photovoltaic system}
A photovoltaic system, also photovoltaic power system, solar PV system, PV system or casually solar array, is a power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and directly convert sunlight into electricity, a solar inverter to change the electrical current from DC to AC, as well as mounting, cabling and other electrical accessories to set-up a working system. It may also use a solar tracking system to improve the system's overall performance or include an integrated battery solution, as prices for storage devices are expected to decline. Strictly speaking, a solar array only encompasses the ensemble of solar panels, the visible part of the PV system, and does not include all the other hardware, often summarized as balance of system (BOS).
PV systems range from small, roof-top mounted or building-integrated systems with capacities from a few to several tens of kilowatts, to large utility-scale power stations of hundreds of megawatts. Nowadays, most PV systems are connected to the electrical grid, while stand-alone or off-grid systems only account for a small portion of the market.
Operating silently and without any moving parts or environmental emissions, PV systems have developed into a mature technology that has been used for fifty years in specialized applications, and grid-connected systems have been operating for over twenty years. A roof-top system recoups the invested energy for its manufacturing and installation within 0.7 to 2 years and produces about 95 percent of net clean renewable energy over a 30-year service lifetime.
{slider Solar water heating}
Solar water heating (SWH) or solar hot water (SHW) systems comprise several innovations and many mature renewable energy technologies that have been well established for many years. SWH has been widely used in Australia, Austria, China, Cyprus, Greece, India, Israel, Japan, Jordan, Spain and Turkey.
In a "close-coupled" SWH system the storage tank is horizontally mounted immediately above the solar collectors on the roof. No pumping is required as the hot water naturally rises into the tank through thermosiphon flow. In a "pump-circulated" system the storage tank is ground- or floor-mounted and is below the level of the collectors; a circulating pump moves water or heat transfer fluid between the tank and the collectors.
SWH systems are designed to deliver hot water for most of the year. However, in winter there sometimes may not be sufficient solar heat gain to deliver sufficient hot water. In this case a gas or electric booster is used to heat the water.
{slider LED technology}
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a two-lead semiconductor light source. It is a basic pn-junction diode, which emits light when activated. When a fitting voltage is applied to the leads, electrons are able to recombine with electron holes within the device, releasing energy in the form of photons. This effect is called electroluminescence, and the color of the light (corresponding to the energy of the photon) is determined by the energy band gap of the semiconductor.
Recent developments in LEDs permit them to be used in environmental and task lighting. LEDs have many advantages over incandescent light sources including lower energy consumption, longer lifetime, improved physical robustness, smaller size, and faster switching.
LED-lighting encourages sustainable design in multiple ways. LED bulbs use less energy than conventional light bulbs, LED bulbs last longer (less bulb changes and therefore less waste), they are free of mercury, and they can be used in special lamps that are easier accessible and recyclable.
{slider Solar cell}
A solar cell consists of two layers of silicon. An electric field is created on the border of these layers. Physical processes cause an electric current to flow between metal contacts when they are connected to the silicon layers.
There are different types of solar cells which vary in their use, performance and in the way the silicon layers are manufactured: These are monocrystalline silicon, polycrystalline silicon and thin-film solar cells. Photovoltaic systems usually use crystalline cells due to their higher efficiency.
{/sliders}
Do you have questions or suggestions? Do not hesitate to contact us at any time.
We are glad to help you!
{backbutton}